Morion Nanotech participated in the formulation of the national standard GB/T 43598-2023 'Nanotechnology - Determination of Oxygen Content and Carbon-to-Oxygen Ratio of Graphene Powder by X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy', which was officially released on December 18, 2023, and will come into effect from July 1, 2024. The release of this national standard provides a standardized method for determining the oxygen content and carbon-to-oxygen ratio of graphene powder in the domestic nanotechnology field, offering crucial testing criteria for the graphene-related industry. It aids in promoting quality control and industrial development of graphene materials.

Graphene materials, due to their outstanding electrical, thermal, and mechanical properties, have shown immense industrial application potential in fields such as lithium-ion batteries, integrated circuits, 5G communications, and new display technologies. Among these, the oxygen content and carbon-to-oxygen ratio (C/O) of graphene materials are not only key characteristic parameters affecting their electrothermal performance but also important criteria for distinguishing between graphene and graphene oxide (GO) materials. Additionally, these two parameters can be used to evaluate product quality and determine the reduction degree of reduced graphene oxide (rGO), providing powerful analytical tools for research and applications in relevant fields.
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) is an advanced analytical technique with excellent chemical property identification capabilities and extremely high sensitivity. Because photoelectrons can escape from the material surface within a few nanometers, XPS technology can precisely reveal the state of the material's nanoscale surface. Given that graphene is a typical two-dimensional material with a thickness at the nanoscale level, XPS technology can perform accurate quantitative analysis on it, thereby revealing the atomic ratio of carbon to oxygen in graphene.
In addition, XPS technology offers several clear advantages, such as small sample usage, no need for pre-treatment, fast analysis speed, ability to obtain chemical state information of the measured elements, and minimal sample damage. These features make XPS technology particularly outstanding for routine testing and analysis of graphene materials. Additionally, this technology can determine the distribution of carbon-oxygen (C-O) and carbon-carbon (C-C) chemical bonds, providing crucial evidence for identifying the type of graphene material.
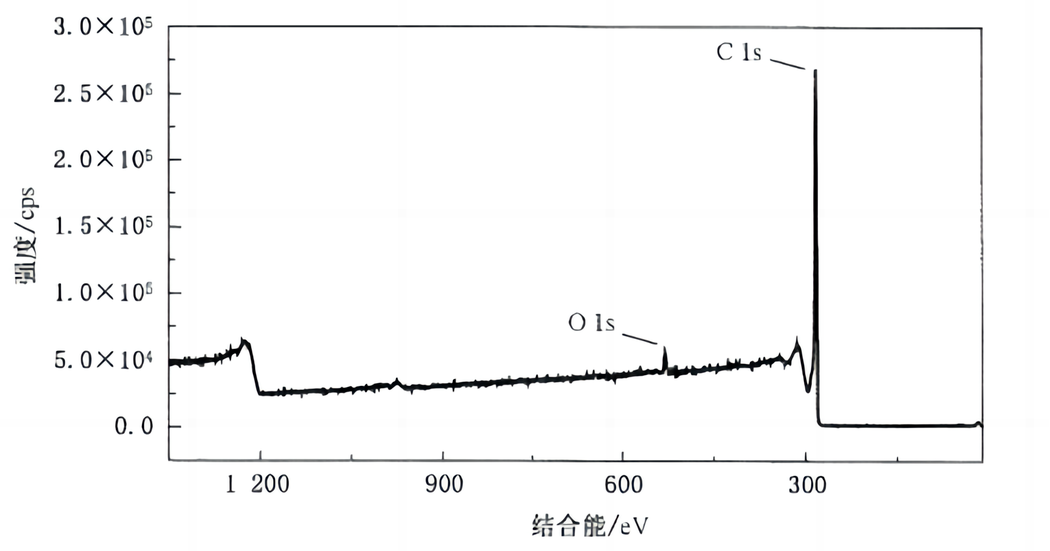
Figure 1 shows the X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) wide scan spectrum of a certain rGO test sample
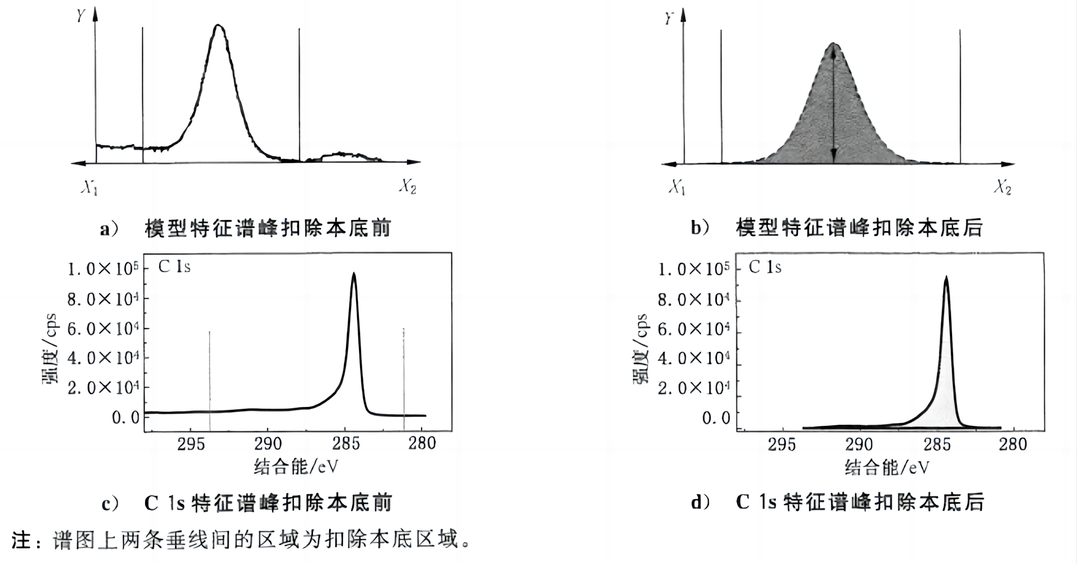
Figure 2 shows a comparison of the C 1s characteristic peak spectrum of a certain rGO sample before and after background subtraction
This standard provides detailed requirements and testing methods for determining the oxygen content and C/O ratio in graphene powder using XPS technology. Considering that GO is destroyed during high-temperature treatment, leading to test data that cannot accurately reflect the sample's condition, Morion Nanotech and the National Center for Nanoscience and Technology, among others, jointly conducted research. After comparing and analyzing XPS tests of GO samples at different pre-treatment temperatures, the pre-treatment conditions for GO samples were determined: the drying temperature must not exceed 60°C, and vacuum treatment time should be no less than 3 hours to ensure the test results accurately reflect the sample's condition. Additionally, this standard offers reference technical indicators for the two core characteristic parameters of oxygen content and C/O ratio, providing crucial technical support for graphene enterprises in developing, producing, and quality controlling graphene materials and related products. This helps upstream and downstream companies in the industry reach consensus on product performance evaluation and specification confirmation.
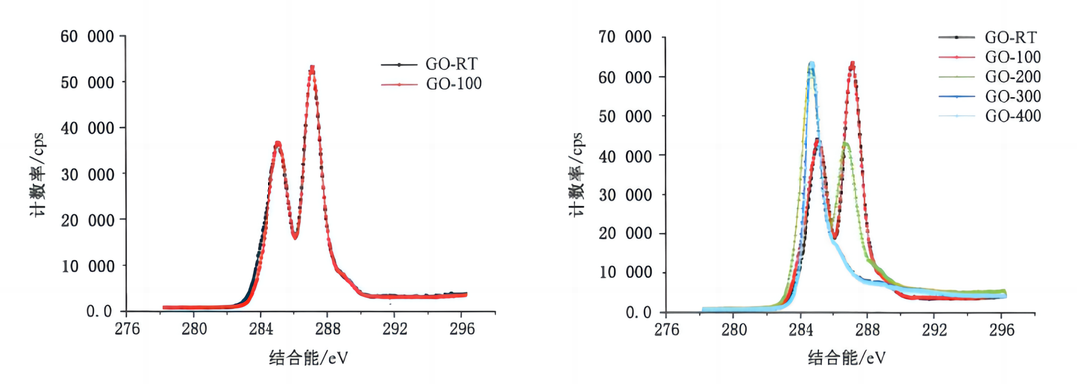
Figure 3: Effect of different pretreatment temperatures on the C 1s characteristic peaks of GO samples
As the scale of graphene material applications grows rapidly and their application fields expand, there is an increasing demand for precise and reliable measurement of oxygen content and C/O ratio in graphene materials. Especially in the two dominant industrial application forms, graphene powder and graphene paste, the requirements for testing accuracy are more stringent. To address this, this standard provides detailed methods for preparing test samples of graphene powder and graphene paste. In Appendix B of this standard, three thoroughly validated powder sample preparation methods are provided: tape sampling, pressed sample preparation, and sample cell preparation. These methods have all been rigorously validated to ensure reliability and accuracy in practical applications. Therefore, users can choose the most suitable sample preparation method based on the specific sample characteristics and testing requirements, without worrying about the accuracy of the test results.
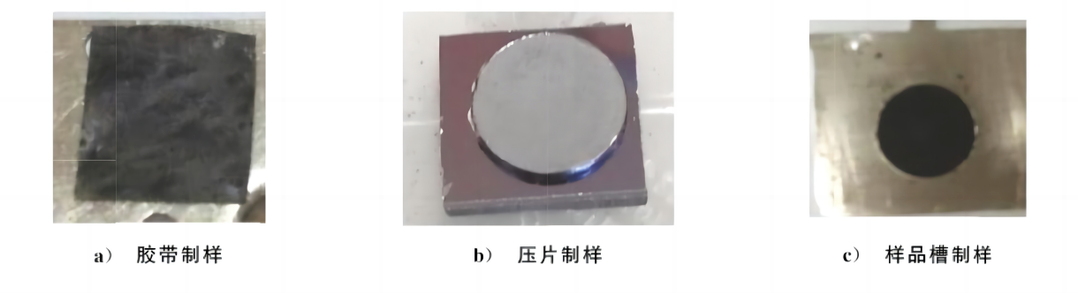
Figure 4: Digital photographs of test samples prepared by different sample preparation methods
Under the call of the national standardization strategy, Morion Nanotech bravely takes on its responsibilities, actively plays a leading role in the field of standardization, and infuses new vitality and rigor into the standard system of the graphene industry. Looking to the future, Morion Nanotech will continue to keep pace with the development of the industry, increase investment in technological innovation, and actively participate in the formulation of national and industry standards, guided by the strategic goals of building a manufacturing power and a quality power, fostering new productive forces, and promoting the graphene industry towards more prosperity and progress.

GB/T 43598-2023:https://openstd.samr.gov.cn/bzgk/gb/newGbInfo?hcno=A3B984A6D97807AF04C726073FE3F26C
 Guangdong Public Security Registration No.44190002005690
Guangdong Public Security Registration No.44190002005690
